Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Pu
Pu O
O powder using master sintering curve theory
powder using master sintering curve theoryNakamichi, Shinya; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 595, p.155072_1 - 155072_11, 2024/07
Oizumi, Akito; Akie, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2023-017, 93 Pages, 2023/12
After the decision of decommissioning JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor), Japan Atomic Energy Agency investigated the possibility to construct a new irradiation test reactor to succeed JMTR (post-JMTR), and the final report of the investigated result was submitted to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology on March 30th 2021. This investigation was carried out in 4 steps of (1) selection of reactor type, (2) reactor core plans studies, (3) neutronic studies, (4) thermal studies, and was finally (5) considered and evaluated. This JAEA-Technology report summarizes the process and the results of (3) neutronic studies. Neutron fluxes were calculated at irradiation sample positions in the investigated cores, the standard core and the compact core, and the calculated fluxes satisfied the required irradiation capability. It was also evaluated the two investigated cores' continuous reactor operation time in days in one refueling cycle, and the results guaranteed an operation days equality with that of existing JMTR. In addition, neutronic characteristics of the cores were estimated, such as power distribution in the core, control rod reactivity worth, reactivity coefficients, distribution of fuel burnup rate of each fuel element, and kinetics parameters. The evaluated neutronic characteristics were used in the post-JMTR final investigation report to confirm the neutronic feasibility by comparing with the neutronic limiting values of existing JMTR, and to estimate the cooling capability to make the core thermally feasible.
Kobayashi, Jun; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ezure, Toshiki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Kurihara, Akikazu; Tanaka, Masaaki
JAEA-Research 2022-009, 125 Pages, 2023/01
The design studies of an advanced loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactor (Advanced- SFR) have been carried out by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). At the core outlet, temperature fluctuations occur due to mixing of hot sodium from the fuel assembly with cold sodium from the control rod channels and radial blanket assembly. These temperature fluctuations may cause high cycle thermal fatigue around a bottom of Upper Internal Structure (UIS) located above the core. Therefore, we conducted a water experiment using a 1/3 scale 60 degree sector model that simulated the upper plenum of the advanced loop-type sodium-cooled reactor. And we proposed some countermeasures against large temperature fluctuations that occur at the bottom of the UIS. In this report, we have summarized that the effect of the countermeasure structure to mitigate the temperature fluctuation generated at the bottom of UIS is confirmed, and the Reynolds number dependency of the countermeasure structure and the characteristics of the temperature fluctuation on the control rod surface.
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1331 - 1344, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reactivity was estimated from a time profile of neutron count rate or a simulated data in a quasi-steady state after sudden change of reactivity or external neutron source strength. The estimation was based on the equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state. The purpose of the study is to develop the method of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. The developed method was applied to the data simulating neutron count rate created by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, and Poisson-distributed random noise and to the transient subcritical experiment data measured by using TRACY. The result shows that the difference of the estimated and reference value was within about 5% or less for (
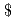
 -1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for
-1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for 
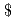
 -1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
-1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
Yoshida, Naoki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2021-011, 12 Pages, 2022/01
In boiling and drying accidents involving high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plants, emphasis is placed on the behavior of ruthenium (Ru). Ru would form volatile species, such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ), and could be released to the environment with coexisting gases, including nitric acid, water, or nitrogen oxides. In this study, to contribute toward safety evaluations of these types of accidents, the migration behavior of gaseous Ru into the liquid phase has been experimentally measured by simulating the condensate during an accident. The gas absorption of RuO
), and could be released to the environment with coexisting gases, including nitric acid, water, or nitrogen oxides. In this study, to contribute toward safety evaluations of these types of accidents, the migration behavior of gaseous Ru into the liquid phase has been experimentally measured by simulating the condensate during an accident. The gas absorption of RuO was enhanced by increasing the nitrous acid (HNO
was enhanced by increasing the nitrous acid (HNO ) concentration in the liquid phase, indicating the occurrence of chemical absorption. In control experiments without HNO
) concentration in the liquid phase, indicating the occurrence of chemical absorption. In control experiments without HNO , the lower the temperature, the greater was the Ru recovery ratio in the liquid phase. Conversely, in experiments with HNO
, the lower the temperature, the greater was the Ru recovery ratio in the liquid phase. Conversely, in experiments with HNO , the higher the temperature, the higher the recovery ratio, suggesting that the reaction involved in chemical absorption was activated at higher temperatures.
, the higher the temperature, the higher the recovery ratio, suggesting that the reaction involved in chemical absorption was activated at higher temperatures.
Kobayashi, Jun; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ezure, Toshiki; Kurihara, Akikazu; Tanaka, Masaaki
Hozengaku, 20(3), p.89 - 96, 2021/10
Hot sodium from the fuel assembly can mix with cold sodium from the control rod (CR) channel and the blanket assemblies at the bottom plate of the Upper Internal Structure (UIS) of Advanced-SFR. Temperature fluctuation due to mixing of the fluids at different temperature between the core outlet and cold channel may cause high cycle thermal fatigue on the structure around the bottom of UIS. A water experiment using a 1/3 scale 60 degree sector model simulating the upper plenum of the Advanced-SFR has been conducted to examine countermeasures for the significant temperature fluctuation generated around the bottom of UIS. We focused on the temperature fluctuations near the primary and backup control rod channels, and studied the countermeasure structure to mitigate the temperature fluctuation through temperature distribution and flow velocity distribution measurements. As a result, effectiveness of the countermeasure to mitigate the temperature fluctuation intensity was confirmed.
Kobayashi, Jun; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ezure, Toshiki; Kurihara, Akikazu; Tanaka, Masaaki
Hozengaku, 20(3), p.97 - 101, 2021/10
Focusing on the thermal striping phenomena that occurs at a bottom of the internal structure of an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor (Advanced-SFR) that has been designed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, a water experiment using a 1/3 scale 60 degree sector model simulating the upper plenum of the Advanced-SFR has been conducted to examine countermeasures for the significant temperature fluctuation generated around the bottom of Upper Internal Structure (UIS). In the previous paper, we reported the effect of measures to mitigate temperature fluctuations around the control rod channels. In this paper, the same test section was used, and a water experiment was conducted to obtain the characteristics of temperature fluctuations around the radial blanket fuel assembly. And the shape of the Core Instrumentation Support Plate (CIP) was modified, and it was confirmed that it was highly effective in alleviating temperature fluctuations around the radial blanket fuel assembly.
Kumagai, Masayoshi*; Akita, Koichi*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 820, p.141582_1 - 141582_9, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:62.81(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Noguchi, Hiroki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kamiji, Yu; Kubo, Shinji; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 137, p.103772_1 - 103772_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2020-014, 33 Pages, 2020/12
Considering the boiling and drying accident of high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plant, Ruthenium (Ru) is an important element. It is because Ru would form volatile compounds such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric oxides (NOx) such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO
) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric oxides (NOx) such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO ). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the effect of NOx on the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO
). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the effect of NOx on the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO (RuO
(RuO (g)). As a result, the RuO
(g)). As a result, the RuO (g) decomposed over time under the atmospheric gasses with NO or NO
(g) decomposed over time under the atmospheric gasses with NO or NO , however, the decomposition rate was slower than the results of experiments without NOx. These results showed that the NOx stabilized RuO
, however, the decomposition rate was slower than the results of experiments without NOx. These results showed that the NOx stabilized RuO (g).
(g).
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.926 - 931, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)An equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state has been derived based on one-point kinetics equations for the purpose of utilizing it for the development of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. It linearly relates power,  , to a new variable
, to a new variable  , which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (
, which is a function of time differential of the power. It has been confirmed by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, that the calculated points (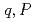 ) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (
) are perfectly in a line described by the new equation and that points (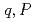 ) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
) calculated from transient subcritical experiments by using TRACY made a line with a slope indicated by the new equation.
Negishi, Hitoshi; Kamide, Hideki; Maeda, Seiichiro; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Abe, Tomoyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(8), p.438 - 441, 2020/08
, 62(8), p.438 - 441, 2020/08
Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, Monju, was under decommission since April, 2018. It is the first time for Japan to make a sodium cooled reactor into decommission. It is significant work and will take 30 years. The Monju has provided wide spectrum and huge amount of findings and knowledge, e.g., design, R&D, manufacturing, construction, and operation up to 40% of full power over 50 years of development history. It is significant to utilize such findings and knowledge for the development and commercialization of a fast rector in Japan.
Aoki, Takeshi; Chirayath, S. S.*; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 141, p.107325_1 - 107325_7, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)The proliferation resistance (PR) of an inert matrix fuel (IMF) in the transuranic nuclear fuel cycle (NFC) of a high temperature gas cooled reactor is evaluated relative to the uranium and plutonium mixed-oxide (MOX) NFC of a light water reactor using PRAETOR code and sixty-eight input attributes. The objective is to determine the impacts of chemical stability of IMF and fuel irradiation on the PR. Specific material properties of the IMF, such as lower plutonium content, carbide ceramics coating, and absence of  U, contribute to enhance its relative PR compared to MOX fuel. The overall PR value of the fresh IMF (an unirradiated direct use material with a one-month diversion detection timeliness goal) is nearly equal to that of the spent MOX fuel (an irradiated direct use nuclear material with a three-month diversion detection timeliness goal). Final results suggest a reduced safeguards inspection frequency to manage the IMF.
U, contribute to enhance its relative PR compared to MOX fuel. The overall PR value of the fresh IMF (an unirradiated direct use material with a one-month diversion detection timeliness goal) is nearly equal to that of the spent MOX fuel (an irradiated direct use nuclear material with a three-month diversion detection timeliness goal). Final results suggest a reduced safeguards inspection frequency to manage the IMF.
Naoe, Takashi; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Xiong, Z.*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.061009_1 - 061009_6, 2020/02
At the J-PARC, a mercury target vessel made of 316L SS suffers proton and neutron radiation environment. The target vessel also suffers cyclic impact stress caused by the proton beam-induced pressure waves. The vessel suffers higher than 4.5 10
10 cyclic loading during the expected service life of 5000 h. We have investigated fatigue strength 316L SS up to gigacycle in the previous studies. The cyclic hardening and softening behavior were observed. In this study, to evaluate the cyclic hardening/softening behavior, the dislocation densities of specimens were measured using the neutron diffraction method at the MLF BL-19. The result showed that the dislocation density of a 316L SS was increased with increasing the number of loading cycles. By contrast, in the case of cold-rolled 316L SS, annihilation and re-accumulation of dislocation by cyclic loading were observed. In the workshop, result of neutron diffraction measurement will be introduced with the progress of fatigue test.
cyclic loading during the expected service life of 5000 h. We have investigated fatigue strength 316L SS up to gigacycle in the previous studies. The cyclic hardening and softening behavior were observed. In this study, to evaluate the cyclic hardening/softening behavior, the dislocation densities of specimens were measured using the neutron diffraction method at the MLF BL-19. The result showed that the dislocation density of a 316L SS was increased with increasing the number of loading cycles. By contrast, in the case of cold-rolled 316L SS, annihilation and re-accumulation of dislocation by cyclic loading were observed. In the workshop, result of neutron diffraction measurement will be introduced with the progress of fatigue test.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(59), p.30832 - 30839, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.23(Chemistry, Physical)Miwa, Kazuji; Takeda, Seiji; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(3-4), p.372 - 375, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)The Ministry of the Environment has indicated the policy of recycling the contaminated soil generated by decontamination activity after the Fukushima accident. By recycling to coastal reclamation which is one of effective recycling application, dissolved radiocesium and absorbed radiocesium on soil particles will flow out to the ocean by construction, therefore evaluating radiocesium transition in ocean considering the both types of radiocesium is important for safety assessment. In this study, the radiocesium outflow during constructing and after constructing is modeled, and radiocesium transition in ocean is evaluated by Sediment model suggested in OECD/NEA. The adaptability of sediment model is confirmed by reproducing evaluation of the coastal area of Fukushima. We incorporate the sediment model to PASCLR2 code system to evaluate the doses from radiocesium in ocean.
Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Review 2018-022, 201 Pages, 2019/01
Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC), Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is conducting technical support to nuclear safety regulation and safety research based on the Mid-Long Term Target determined by Japanese government. This report summarizes the research structure of NSRC and the cooperative research activities with domestic and international organizations as well as the nuclear safety research activities and results in the period from JFY 2015 to 2017 on the nine research fields in NSRC; (1) severe accident analysis, (2) radiation risk analysis, (3) safety of nuclear fuels in light water reactors (LWRs), (4) thermohydraulic behavior under severe accident in LWRs, (5) materials degradation and structural integrity, (6) safety of nuclear fuel cycle facilities, (7) safety management on criticality, (8) safety of radioactive waste management, and (9) nuclear safeguards.
Udagawa, Makoto; Li, Y.; Nishida, Akemi; Nakamura, Izumi*
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 167, p.2 - 10, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.86(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)It is important to assure the structural Integrity of piping systems under severe earthquakes because those systems comprise the pressure boundary for coolant with high pressure and temperature. In this study, we examine the seismic safety capacity of piping systems under severe dynamic seismic loading using a series of dynamic-elastic-plastic analyses focusing on dynamic excitation experiments of 3D piping systems which was tested by NIED. Analytical results were consistent with experimental data in terms of natural frequency, natural vibration mode, response accelerations, elbow opening-closing displacements, strain histories, failure position, and low-cycle fatigue failure lives. Based on these results, we concluded that the analytical model used in the study can be applied to failure behavior evaluation for piping systems under severe dynamic seismic loading.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Suyama, Kenya; Ryufuku, Susumu*
JAEA-Review 2017-010, 93 Pages, 2017/06
There is an ongoing discussion on the application of burnup credit to the criticality safety controls of facilities that treat spent fuels. With regard to such application of burnup credit in Japan, this document summarizes the current technical status of the prediction of the isotopic composition and criticality of spent fuels, as well as safety evaluation concerns and the current status of legal affairs. This report is an English translation of A Guide to Introducing Burnup Credit, Preliminary Version, originally published in Japanese as JAERI-Tech 2001-055 by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facility Safety Research Committee.
Akita, Koichi; Shibahara, Masakazu*; Ikushima, Kazuki*; Nishikawa, Satoru*; Furukawa, Takashi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Vladimir, L.*
Yosetsu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 35(2), p.112s - 116s, 2017/06